×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Audi Parts

My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Audi Relay Boxes
Relay Block- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
47 Relay Boxes found
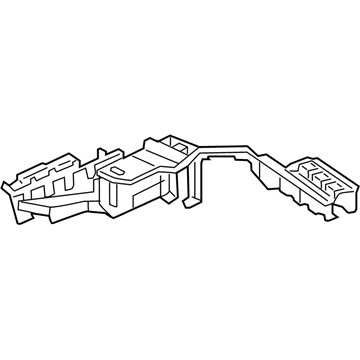
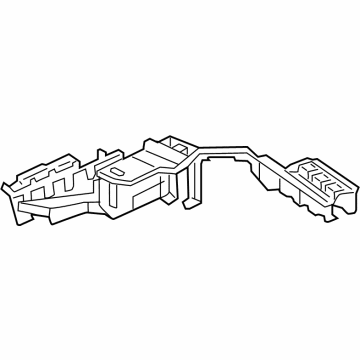
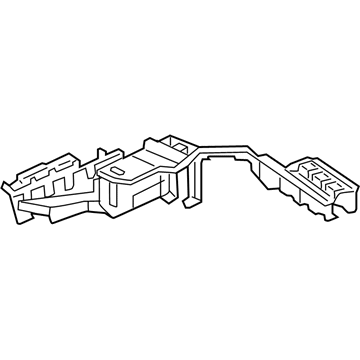
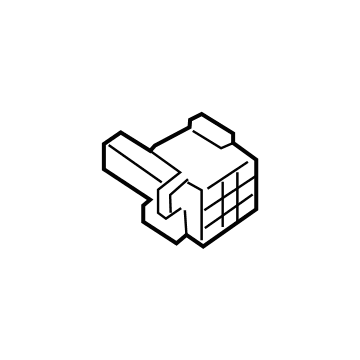
Audi Relay Box Part Number: 4K0-907-285-A
$21.86 MSRP: $34.98You Save: $13.12 (38%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Bracket; Relay Box
Audi Relay Box Part Number: 4K0-907-285-B
$21.86 MSRP: $34.98You Save: $13.12 (38%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Bracket; Relay Box
Audi Relay Box Part Number: 4K0-907-285-C
$23.11 MSRP: $36.98You Save: $13.87 (38%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Bracket; Relay Box
Audi Relay Box Part Number: 5WA-941-824-B
$27.74 MSRP: $44.37You Save: $16.63 (38%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Plate; Relay Box
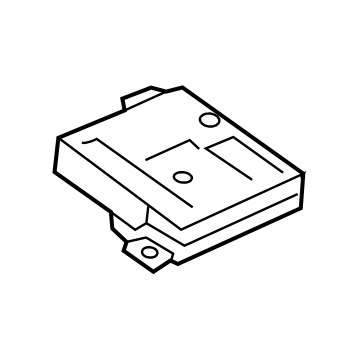
Audi Relay Plate Part Number: 4H0-937-527
$1.32 MSRP: $2.06You Save: $0.74 (36%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Plate; Holder, Relay Box
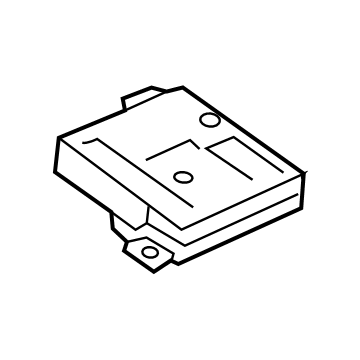
Audi Relay Plate Part Number: 5Q0-937-507-A
$10.91 MSRP: $17.04You Save: $6.13 (36%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Plate
Audi Relay Plate Part Number: 5Q0-937-507-B
$10.91 MSRP: $17.04You Save: $6.13 (36%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Plate; Relay Box
Audi Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: 4G0-971-845-A
$69.01 MSRP: $96.65You Save: $27.64 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Mounting; Fuse & Relay Box
Audi Relay & Fuse Plate Part Number: 5Q0-937-615-C
$223.71 MSRP: $313.32You Save: $89.61 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Holder; Fuse Holder, Relay Fuse Plate
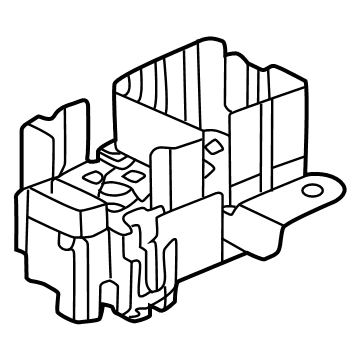
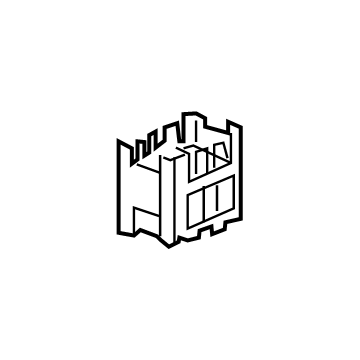
Audi Junction Block Part Number: 4K0-937-517
$78.53 MSRP: $109.99You Save: $31.46 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Junct Box; Junction Block
Audi Junction Block Part Number: 4K0-937-517-A
$78.53 MSRP: $109.99You Save: $31.46 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Junct Box; Junction Block
Audi Junction Block Part Number: 4K0-937-517-AC
$78.53 MSRP: $109.99You Save: $31.46 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Junct Box; Junction Block
Audi Junction Block Part Number: 4K0-937-517-B
$78.53 MSRP: $109.99You Save: $31.46 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Junct Box; Junction Block
Audi Junction Block Part Number: 4K0-937-517-C
$78.53 MSRP: $109.99You Save: $31.46 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Junct Box; Junction Block
Audi Junction Block Part Number: 4K0-937-517-D
$78.53 MSRP: $109.99You Save: $31.46 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Junct Box; Junction Block
Audi Junction Block Part Number: 4K0-937-517-E
$78.53 MSRP: $109.99You Save: $31.46 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Junct Box; Junction Block
Audi Junction Block Part Number: 4K0-937-517-F
$78.53 MSRP: $109.99You Save: $31.46 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Junct Box; Junction Block
Audi Junction Block Part Number: 4K0-937-517-G
$78.53 MSRP: $109.99You Save: $31.46 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Junct Box; Junction Block
Audi Junction Block Part Number: 4K0-937-517-H
$78.53 MSRP: $109.99You Save: $31.46 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Junct Box; Junction Block
Audi Junction Block Part Number: 4K0-937-517-R
$78.53 MSRP: $109.99You Save: $31.46 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Junct Box; Junction Block
| Page 1 of 3 |Next >
1-20 of 47 Results
Audi Relay Boxes
The Audi Relay Box is a very important part of your vehicle. Therefore, it has to be maintained in good condition to avoid performance issues and comfortable driving. And these regular checks and replacements will ultimately save you some big repair costs. It is better to choose OEM parts when it comes to the time for fixing them. Why? Because they fit perfectly well and ensure safety. For people who prefer doing their maintenance, the genuine Audi Relay Box is quite perfect. At AudiPartsGiant.com, we specialize in genuine Audi Relay Boxes only. Also, we offer an extensive online catalog with many categories, ample stock, and secure shopping. The Audi Relay Box is shipped directly from authorized Audi dealers at competitive prices. So trust us, and we will give you nothing but superior service. Depend on us for all your genuine parts needs, and then we will keep your automobile moving smoothly.
Audi Relay Boxes Parts and Q&A
- Q: How do Fuse Box and Relay Boxes protect circuits from excessive current flow on Audi A3?A:Fuses are set up to interrupt a circuit once a specific current level is surpassed as a safety measure to prevent damage to components and wiring in case of too much current flow, which is normally as a result of a fault such as a short-circuit. The fusebox is on the drivers side of the facia; it is accessed by unclipping the fusebox cover when the driver has opened the door with the positions of the fuses indicated on the back of the cover. Enabling the removal of a fuse, it is necessary to switch off the circuit or ignition and then extract the fuse out of the terminals, a blown fuse will have a piece of wire or be melted. Never use a fuse of a different rating, but it is always possible to replace them with the right rating. The bottom has a stamped fuse rating which is colour-coded. When the fuse keeps blowing, locate the cause of the inconvenience and then install the same fuse once more, because in this case, short to earth caused by insulation defects is probable. To circuits which have only one fuse, isolate the fault by turning on the circuits until the fuse blows once more, and have spare fuses of the appropriate value in the car. Further fuses and relays can be found in the fusebox high up on the left of the engine compartment, which has an unclipped fuse holder cover. To replace a fusible link, remove the negative terminal of the battery, unscrew the retaining nuts, remove the blown link, replace it with a new one, reconnect the lead, make sure that the retaining nuts go into place, replace them and install them again and fix the battery. A relay is a switch, controlled by electricity, which may turn heavy current on and off remotely, may have many inputs to control it, may have timer facilities. Another connection is that most of the relays are in the relay plate behind the driver side facia, and the other relays in the engine compartment fusebox. To gain access to the relays one has to take the lower facia of the driver side panel away. When a circuit operated by a relay faults, use the system to see whether the relay clicks when energised, in this case the fault is in the components or wiring of the system. When the relay does not energise it is possible that it is not being powered or is faulty and this can be tested by replacing it with a known good unit. To remove a relay, make sure that the corresponding circuit is switched off then pull it out of the socket and squeeze it back. The hazard-warning switch is provided with a direction indicator/hazard flasser relay.
- Q: Where are the Fuse Box and Relay Boxes located, and how can they be accessed and replaced on Audi 100?A:Fuses are found in the fusebox behind the end cover on the driver's side of the facia panel, with additional fuses, including automatic circuit breakers, located in the fuse/relay box in the rear corner of the engine compartment. More fuses can be accessed behind the front footwell side trim panels and the footwell floor plastic cover. To access the fusebox, open the driver's side door and unclip the end cover from the facia. For the engine compartment fuses, release the retaining clip and remove the cover from the fuse/relay box. Each fuse protects specific circuits, and to remove a fuse, switch off the relevant circuit or ignition, then pull the fuse out; a blown fuse will show a broken or melted wire. Always replace a fuse with one of the same rating, as indicated on the fuse, and avoid using a different rating or substituting anything else. If a new fuse blows immediately, investigate the cause, as faulty insulation may be the issue. Spare fuses of each relevant rating should be kept in the vehicle. Most relays are located in the fuse/relay box in the engine compartment or behind the driver's side facia storage compartment panel and footwell side trim panels. Access to the engine compartment relays is gained by removing the lid, while those behind the driver's side storage compartment require removing retaining screws and the panel. To access footwell trim panels, remove the trim strip and screws, with relay details available on a sticker on the rear of the panel. If a relay-controlled circuit develops a fault, listen for a click when the system is operated; if no click is heard, the relay may not be receiving power or could be faulty. Testing can be done by substituting with a known good relay, keeping in mind that while some relays may look identical, they can perform different functions. To replace a relay, ensure the ignition is off, pull out the old relay, and press in the new one.
Related Audi Parts
Browse by Model
100 Quattro Relay Boxes 100 Relay Boxes 90 Quattro Relay Boxes 90 Relay Boxes A3 Quattro Relay Boxes A3 Relay Boxes A3 Sportback e-tron Relay Boxes A4 Quattro Relay Boxes A4 Relay Boxes A4 allroad Relay Boxes A5 Quattro Relay Boxes A5 Sportback Relay Boxes A6 Quattro Relay Boxes A6 Relay Boxes A6 allroad Relay Boxes A7 Quattro Relay Boxes A7 Sportback Relay Boxes A8 Quattro Relay Boxes A8 Relay Boxes Cabriolet Relay Boxes Q3 Quattro Relay Boxes Q3 Relay Boxes Q4 e-tron Relay Boxes Q4 e-tron Sportback Relay Boxes Q5 PHEV Relay Boxes Q5 Relay Boxes Q7 Relay Boxes Q8 Relay Boxes Q8 e-tron Relay Boxes Q8 e-tron Sportback Relay Boxes R8 Relay Boxes RS Q8 Relay Boxes RS3 Relay Boxes RS5 Relay Boxes RS5 Sportback Relay Boxes RS6 Avant Relay Boxes RS7 Relay Boxes RS7 Sportback Relay Boxes S3 Relay Boxes S4 Relay Boxes S5 Relay Boxes S5 Sportback Relay Boxes S6 Relay Boxes S7 Relay Boxes S7 Sportback Relay Boxes S8 Relay Boxes SQ5 Relay Boxes SQ7 Relay Boxes SQ8 Relay Boxes TT Quattro Relay Boxes TT RS Quattro Relay Boxes TT Relay Boxes TTS Quattro Relay Boxes e-tron Quattro Relay Boxes e-tron S Relay Boxes e-tron S Sportback Relay Boxes e-tron Sportback Relay Boxes